Climate Change
Korea has experienced changes in its climate due to global warming caused by human activities. One of the most significant changes is the shift towards a subtropical climate in certain regions, including Seoul, where Gyeongbokgung Palace is located. This shift has occurred due to a combination of factors, including rising temperatures, changing precipitation patterns, and increased humidity.
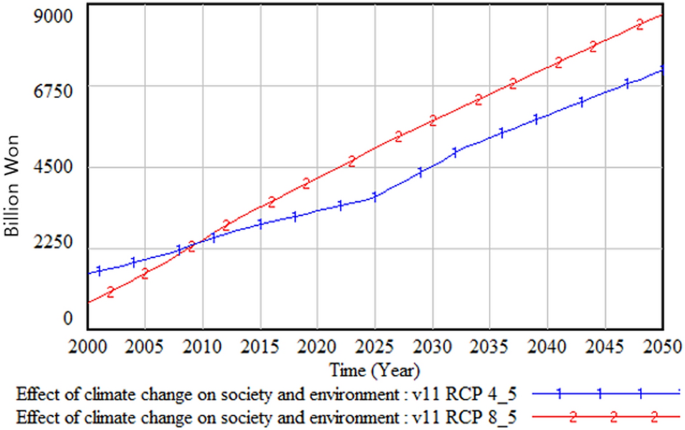
The average temperature in Korea has risen by approximately 1.1 degrees Celsius over the past century, with the most significant increases occurring in the winter months. This increase in temperature has resulted in longer and hotter summers, with more frequent heatwaves and droughts. In addition to temperature changes, precipitation patterns have also shifted, with more intense rainfall events and longer dry spells. These changes have led to an increase in humidity, which is particularly problematic for traditional wooden structures like Gyeongbokgung Palace.
Termites
“Termites Threaten Timber Heritage”
Humidity levels in Seoul have been increasing steadily over the past few decades, with an average annual relative humidity of 65%. Higher humidity levels provide ideal conditions for termites to thrive and reproduce, as they require moisture to survive. This leading to significant damage to traditional wooden structures like Gyeongbokgung Palace. It is essential to address the root causes of climate change and take steps to mitigate its impact on cultural heritage sites like Gyeongbokgung Palace to ensure their preservation for future generations.


In recent years, the palace has been facing a serious threat from climate change, which has caused a significant increase in the population of termites. Termites are known for their ability to feed on wood, and they are a major problem for traditional wooden structures like Gyeongbokgung Palace. As the climate in Korea becomes warmer and more humid due to climate change, it creates an ideal environment for termites to thrive.
The damage caused by termites to Gyeongbokgung Palace is extensive and can be seen in many areas of the palace. The wooden structures of the palace, such as the gates, walls, and roofs, have been severely damaged by termites. The termites feed on the wood, weakening the structures and making them vulnerable to collapse. The damage caused by termites is not limited to the structural components of the palace but also extends to the cultural artifacts and objects housed inside the palace.
Climate change is causing a significant increase in the population of termites, which is having a serious impact on traditional wooden structures like Gyeongbokgung Palace. The damage caused by termites to the palace is extensive and can be seen in many areas of the palace.
It is imperative to continue monitoring and addressing the impact of climate change on cultural assets like Gyeongbokgung Palace to ensure their preservation for future generations.

Leave a Reply