The threats of climate change
European climate change projections to 2050
Warming
Europe could be warmer than the world average
by 2050.
Drought
Insufficient surface water due to higher
temperatures can trigger drought.
Flooding
Climate change affects global precipitation Localised excessive precipitation can cause flooding.
How climate change will affect the Acropolis
Global
warming
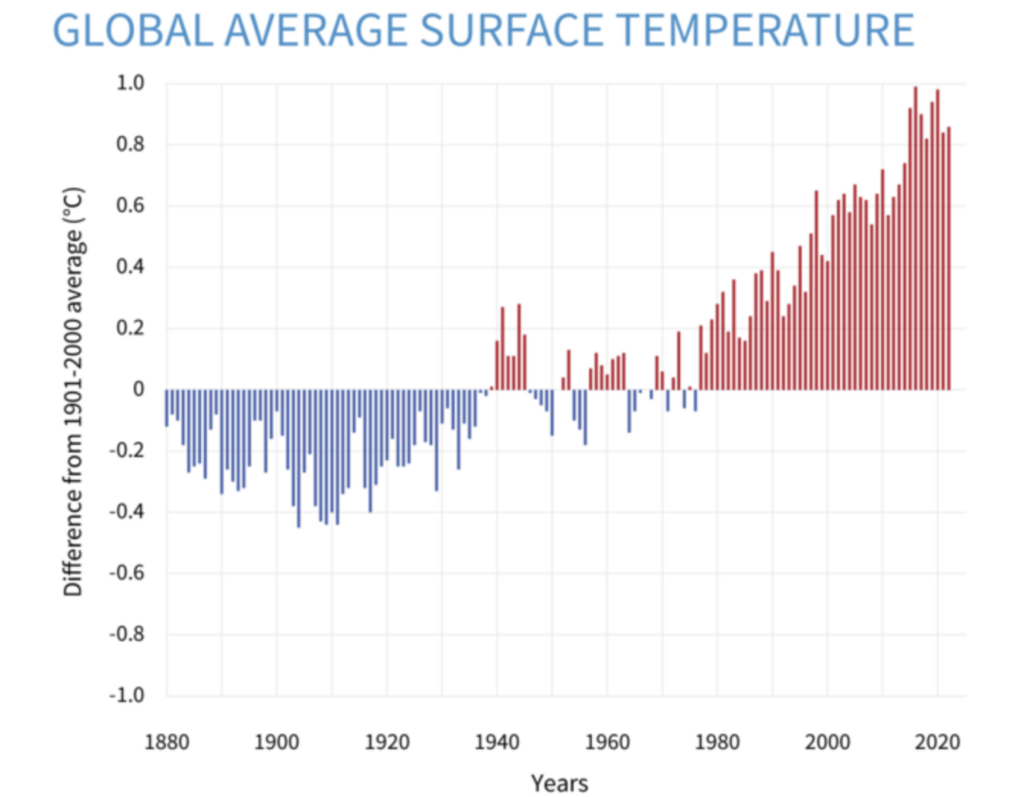
Given the enormous scale and heat capacity of the global ocean, a significant amount of heat is required to raise the Earth’s annual average surface temperature, even by a small amount. Since the preindustrial era (1880-1900), the approximately 2 degrees Fahrenheit (1 degree Celsius) rise in global average surface temperature may seem small, but it represents a significant increase in accumulated heat.
This additional heat is driving regional and seasonal extreme temperatures, reducing snow cover and sea ice, intensifying heavy precipitation events, and altering the range of habitats for plants and animals – expanding some and shrinking others. As shown in the figure, warming rates are faster in most land areas than in most ocean areas, and warming is occurring more rapidly in the Arctic region than in most other regions.


Rainfall
variation
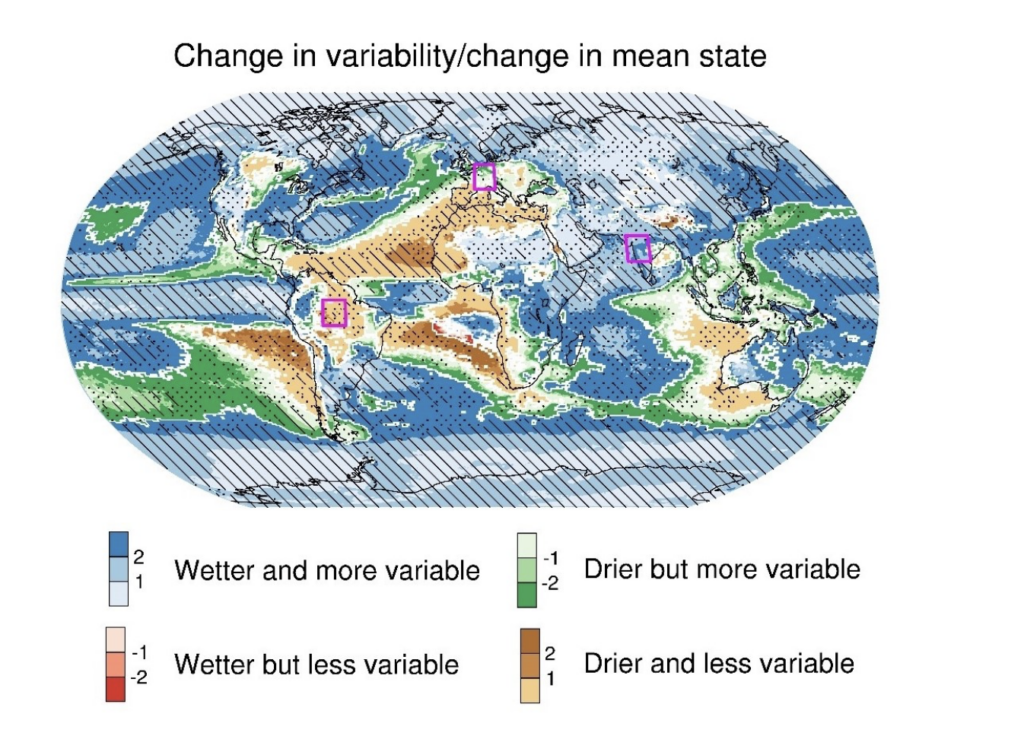
A collaborative study between China and the United Kingdom found that in a warming world, about two-thirds of the land is expected to experience a climate that is not only wetter, but also more variable between wet and dry conditions. This was found for all time scales of precipitation variability, including day-to-day, month-to-month, and year-to-year. In most parts of these areas, the increase in rainfall variability is expected to be greater than the increase in average rainfall. This means that extreme wet and dry regions, such as floods and droughts, may increase, with a broader and faster transition range between them.
Wenxia commented that “if the increase in rainfall variability challenges the climate resilience of infrastructure, human society and ecosystems, it will make adapting to climate change even more difficult.” This is because the expected changes in rainfall are expected to increase with the increase in global temperature.
Global precipitation over 20 years
Rising
sea-levels

Due to anthropogenic global warming, global sea levels are rising, with the most recent sea level in over 2500 years. Sea level rise is primarily caused by two factors related to global warming: water from melting ice sheets and glaciers, and expansion of seawater as it warms. The left figure tracks the changes in global sea levels observed by satellites since 1993.
Athens is located near the sea, and sea level rise could cause a series of problems for Athens and its surrounding areas. As global temperatures rise, sea level rise caused by melting glaciers and expanding seawater has become one of the main impacts of global warming. If sea levels rise, Athens may be affected by problems such as flooding, coastal erosion, and island submersion. These issues could seriously impact Athens’ infrastructure and tourism industry, thereby having a negative effect on the city’s economic and social development. Additionally, sea level rise may have far-reaching effects on Athens’ ecosystems, including changes to coastal wetlands and marine ecosystems.
The impact of climate change on the Acropolis
- Weathering: Climate change caused by global warming may increase precipitation and humidity, which could lead to weathering and corrosion of buildings and statues on the Acropolis.
- Geological hazards: The Acropolis is located in the Greek Mediterranean region, which has a high risk of earthquakes and other geological hazards. Global warming may increase the likelihood of geological hazards such as earthquakes and landslides, which could cause damage to the Acropolis’ buildings.
- Sea-level rise: As global temperatures rise, glacier melting and sea-level expansion could cause sea levels to rise. The Acropolis is located close to the sea, and sea-level rise could cause flooding and other problems in and around the Acropolis.
- Tourism industry: The Acropolis is one of the most famous tourist attractions in Greece. Global warming may affect tourists’ travel plans, especially in the case of high temperatures during the summer. In addition, changing climates may affect the surrounding ecosystems of the Acropolis, which could affect the tourism industry.
It is worth noting that these impacts are not unique or inevitable. However, with the continued development of global warming and climate change, these impacts may become increasingly significant.