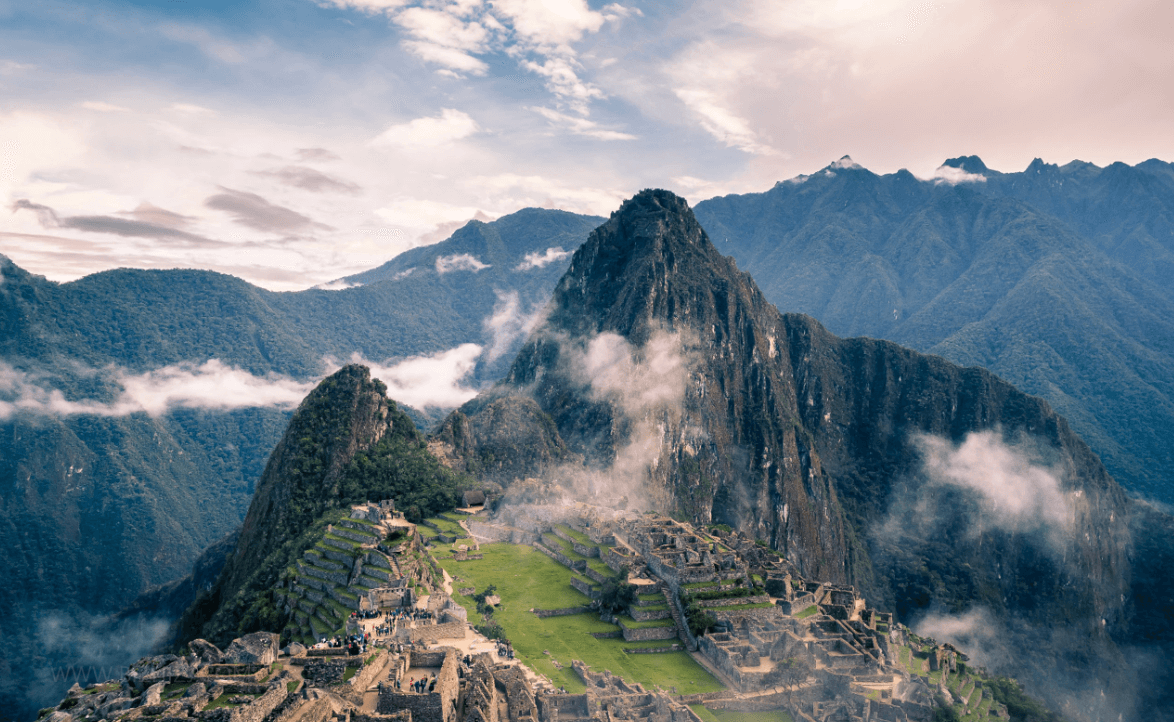

Machu Picchu Ancient Temple
Machu Picchu, located in the Andes Mountains of Peru, is an ancient Inca site considered one of the most breathtaking architectural marvels of the Inca Empire. This mysterious and magnificent site is believed to have served as a religious, political, and cultural center during the Inca Empire, and is also one of the most significant archaeological sites in the world. Its stunning landscapes, enigmatic ambiance, and ancient history attract visitors from all over the globe to explore and experience it. This ancient temple leaves behind countless mysteries and stories, forever captivating the imagination.
Temple of the Sun
The Temple of the Sun is located at the center of Machu Picchu, built atop a small cave, opposite to the Temple of the Moon. It is one of the iconic structures of Machu Picchu and one of the most renowned sun temples among the surviving Inca ruins. The Temple of the Sun represents the Inca’s profound knowledge of astronomy and architecture, a marvel created through their wisdom.
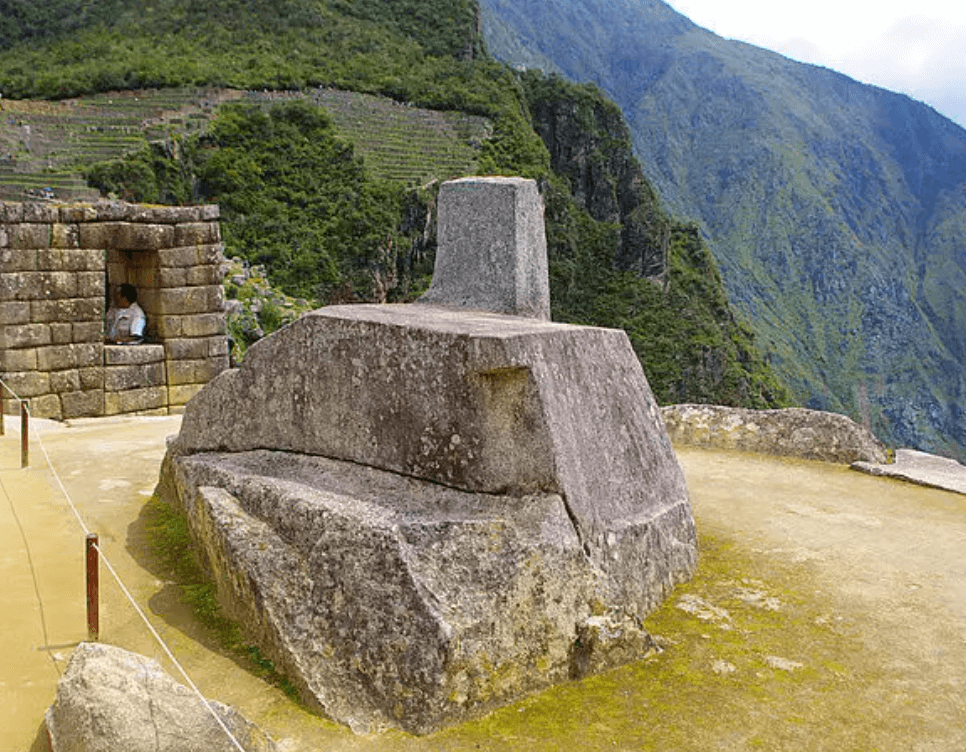


Hitching Post of the Sun
The “Hitching Post of the Sun,” a famous feature of Inca culture, is located on the altar of Machu Picchu’s ancient city. It is a rectangular stone, polished smooth with precise angles, facing towards the east. This hitching post is a special astronomical device. The Incas used the changing shadows cast by the Hitching Post of the Sun to determine seasons and create calendars.
Temple of the Condor
The Temple of the Condor is an important religious relic of Machu Picchu, showcasing the craftsmanship of Inca stonemasons. Formed from rocks millions of years old, in the hands of skilled Inca artisans, these natural formations were sculpted into the image of a soaring condor, symbolizing divine power and significance.
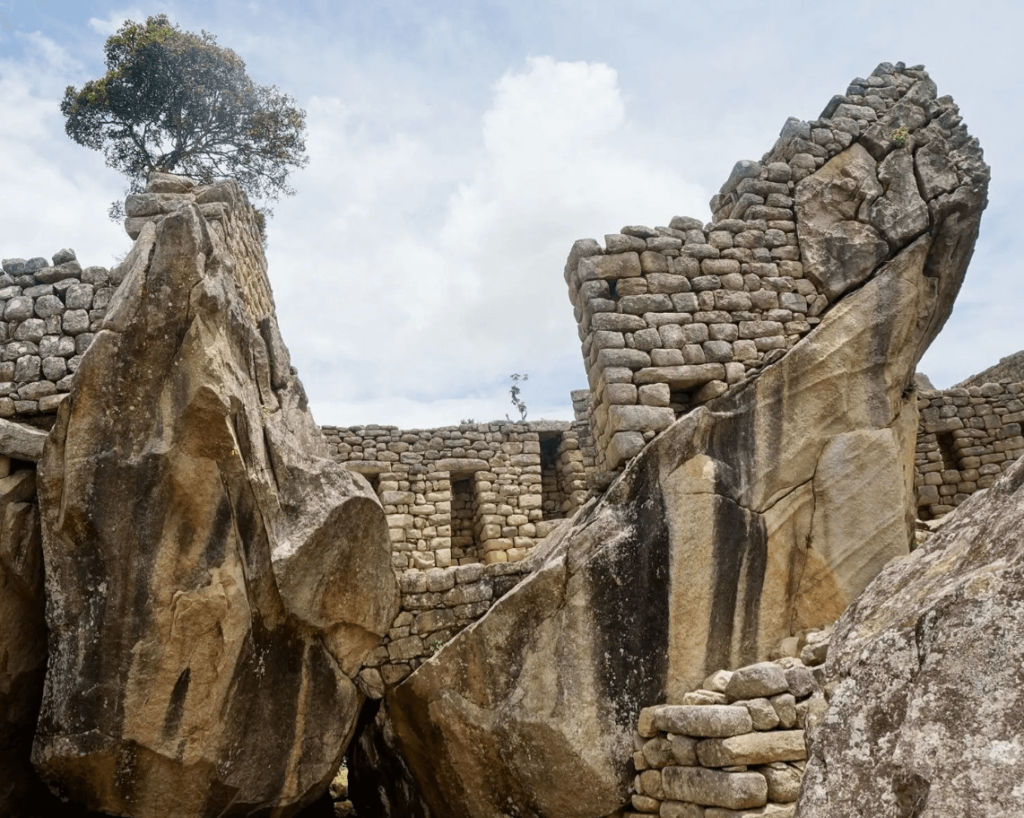


Temple of the Three Windows
The Temple of the Three Windows, located in the central area of Machu Picchu, is named for the three large stone windows stacked on a massive stone wall. It is one of the most important sacred sites of Machu Picchu.
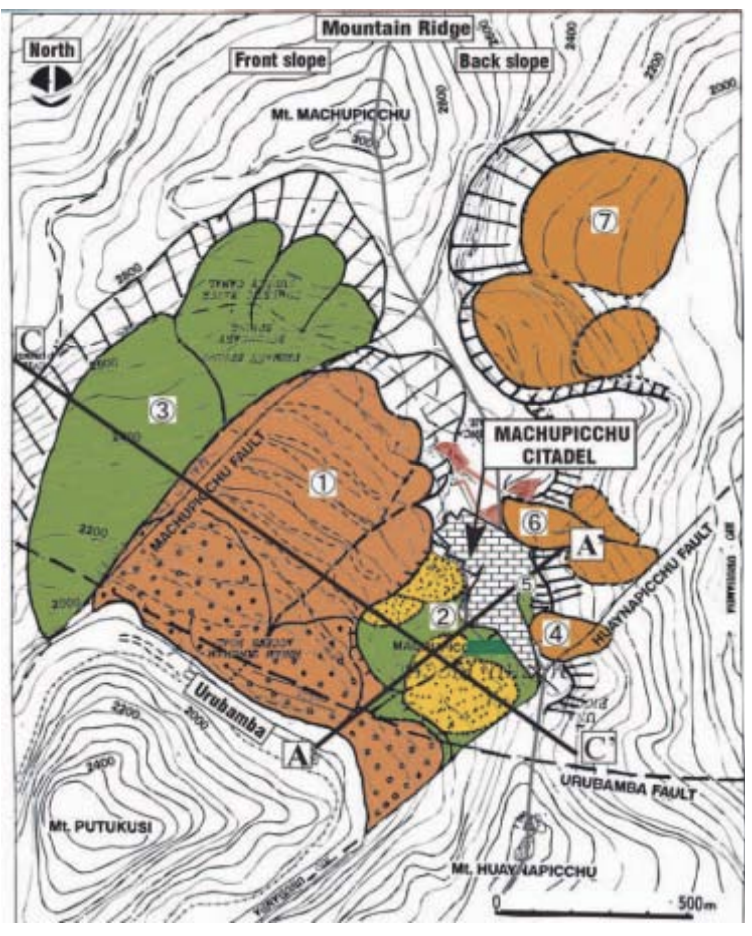
Landslides and potential landslides around the Machu Picchu Citadel (Sassa
et al.2001)
Cusco, Peru.
Landslide Risk in Machu Picchu
Machu Picchu faces the danger of mountainous landslides due to its location in the Andes Mountains. The region is prone to seismic activity and heavy rainfall, both of which can contribute to destabilizing the slopes surrounding the site. Additionally, the presence of steep cliffs and the natural erosion processes inherent in mountainous terrain further heighten the risk of landslides. These hazards pose a continuous threat to the preservation of Machu Picchu and necessitate ongoing efforts to monitor and mitigate the risks posed by geological instability.
The hazards of earthquakes
Machu Picchu is situated in a seismic active zone in South America, where seismic activity is primarily caused by the interaction between the Nazca Plate and the South American Plate. Machu Picchu is composed of multiple finely crafted stone structures, and seismic vibrations from earthquakes can potentially loosen stones or create structural cracks, jeopardizing the stability of the entire site. The shaking induced by earthquakes can also compromise the protective measures of the buildings, accelerating the aging and damage of construction materials.
Earthquakes in various magnitude ranges from instrumental
records.(M. B. Karkee, 2005)
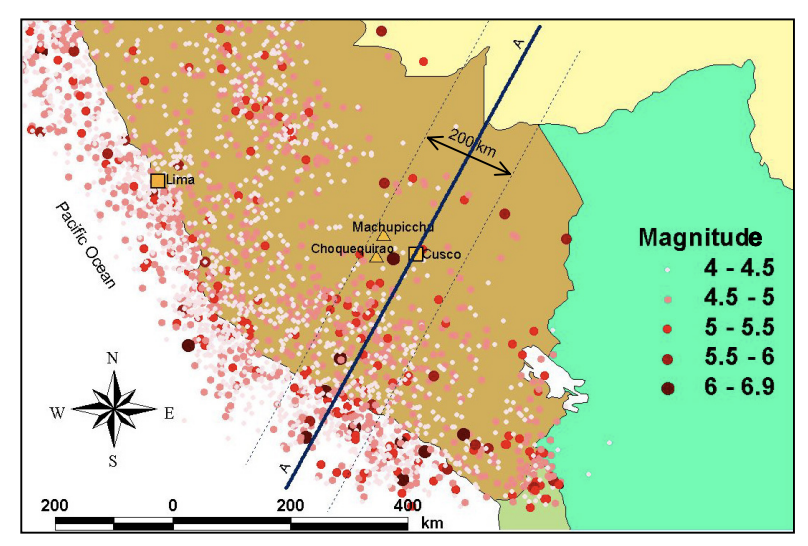
Earthquakes in various magnitude ranges from instrumental
records.(M. B. Karkee, 2005)

SDG 8.9:Promote Beneficial and Sustainable Tourism
Machu Picchu has faced negative impacts from tourism, highlighting the importance of achieving Sustainable Development Goal 8.9, which promotes beneficial and sustainable tourism practices. Implementing responsible tourism management and engaging local communities are essential steps in mitigating these challenges and preserving Machu Picchu’s cultural and environmental heritage.
SDG 11.4:Protect the Worlds Cultural and Natural Heritage
This goal emphasizes the importance of balancing tourism and preservation efforts to ensure the long-term integrity of Machu Picchu’s unique cultural and environmental heritage.

Proudly powered by WordPress