The Longmen Grottoes, located in Luoyang, Henan Province, China, are one of the finest examples of Chinese Buddhist art. The site comprises the West Hill Grottoes, the East Hill Grottoes, Bai Garden, and Xiangshan Temple. Carved into limestone cliffs along the Yi River, the site features over 2,300 caves and niches filled with thousands of Buddha statues, inscriptions, and steles dating back to the Northern Wei and Tang dynasties. Recognized by UNESCO as the pinnacle of Chinese stone carving art, the grottoes reflect artistic, spiritual, and cultural achievements spanning centuries.

The Longmen Grottoes Scenic Area mainly consists of four major attractions: the Xishan Grottoes, the Dongshan Grottoes, Bai Garden, and Xiangshan Temple. The following sections will introduce them in this order.
Overall Route: West Hill Grottoes → East Hill Grottoes → Xiangshan Temple → Bai Garden
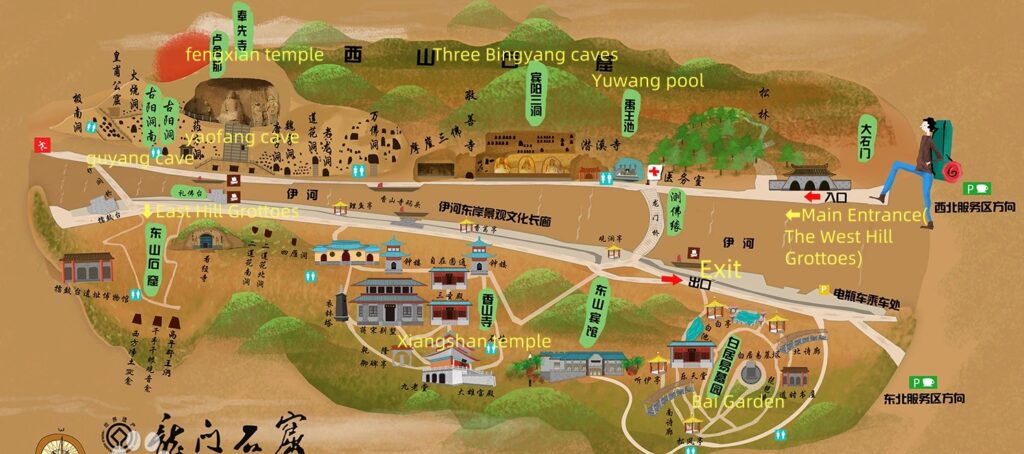
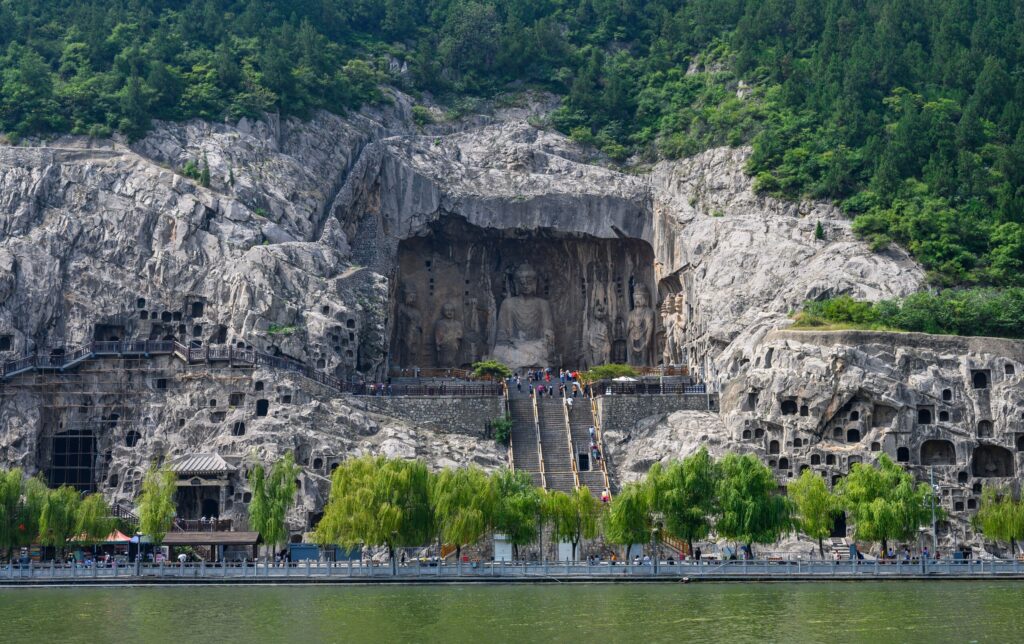
the West Hill Grottoes:
- Three Binyang Caves: The most representative large-scale imperial cave of the Northern Wei period was constructed by Emperor Xuanwu to offer blessings for his parents, Emperor Xiaowen and Empress Wenzhao.
- Wanfo Cave (Ten Thousand Buddha Cave): The Cave of Ten Thousand Buddhas was named for the 15,000 small Buddha statues neatly arranged on its northern and southern walls.
- Fengxian Temple: The largest, most magnificent, and most artistically exquisite group of cliffside sculptures in the Longmen Grottoes.

Guyang Cave: It is the earliest cave to be carved in the Longmen Grottoes, with the longest span of construction and the most abundant content.
Yaofang Cave (Prescriptions Cave): Yaofang Cave contains the earliest known stone-carved medical prescriptions in China.
Lotus Cave: The Lotus Cave is renowned for its intricately carved lotus flower on the ceiling, symbolizing purity and the spiritual essence of Buddhism.
Longmen Bridge: Longmen Bridge spans the Yi River, offering a picturesque view of the grottoes and connecting visitors to both sides of this historic site.
Yu wang Pool: Yu Wang Pool is a serene natural spring near the grottoes, historically linked to Emperor Yu’s legendary flood control efforts in Chinese mythology.
The East Hill Grottoes
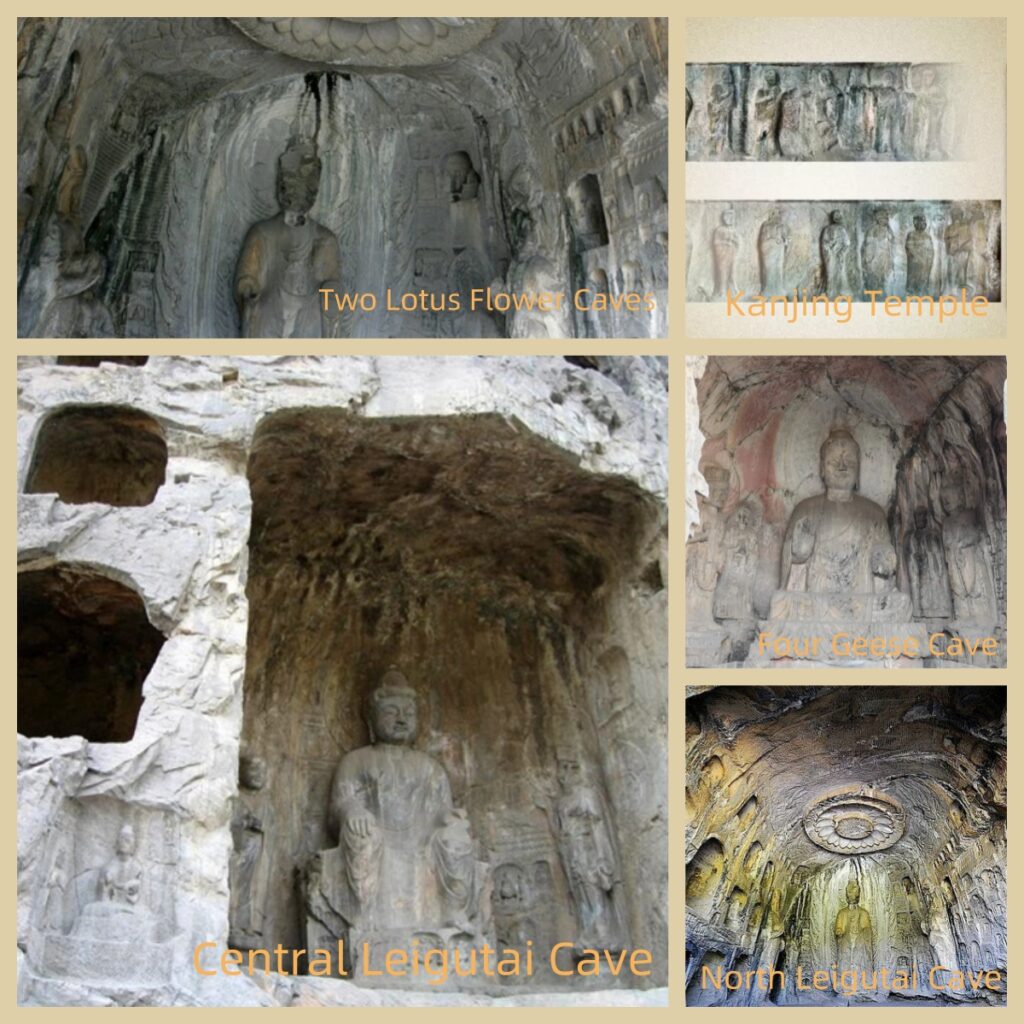
Central Leigutai Cave: The main cave at Leigutai features a large seated Buddha.
North Leigutai Cave:A cave with rows of small Buddha niches carved into the walls.
Kanjing Temple: An ancient temple where monks once recited and studied scriptures.
Four Geese Cave: A cave named for its four carved goose statues.
Two Lotus Flower Caves: Two facing caves with lotus flower carvings on the ceilings.

The Xiangshan Temple:

Xiangshan Temple is located in the western valley of Xiangshan Mountain, 13 kilometers south of Luoyang City
The Bai Garden:

Located on Pipa Peak of the East Hill in the Longmen Scenic Area of Luoyang, it is the tomb garden of the Tang dynasty poet Bai Juyi, covering an area of 30,000 square meters.

Climate Threats to the Longmen Grottoes
- Extreme weather and heavy rainfall can accelerate the weathering of rocks and cause corrosive damage to the structure of the limestone.
- Thermal expansion and contraction caused by large temperature differences between day and night or seasonal changes can further age and deteriorate the surface of the stone carvings.
- Due to the proximity to the Yi River, the humid environment has led to biological weathering inside the grottoes, such as the growth of moss and mold. In some cases, plants can also damage the appearance of the carvings.

The Longmen Cultural Relics Administration has already taken measures to protect and reinforce the Longmen Grottoes.

SDG 11.4: Strengthen efforts to protect and safeguard the world’s cultural and natural heritage,
SDG 13.1 / 13.3: Enhance resilience to climate-related hazards and disasters, and improve public awareness and capacity for climate change mitigation and adaptation
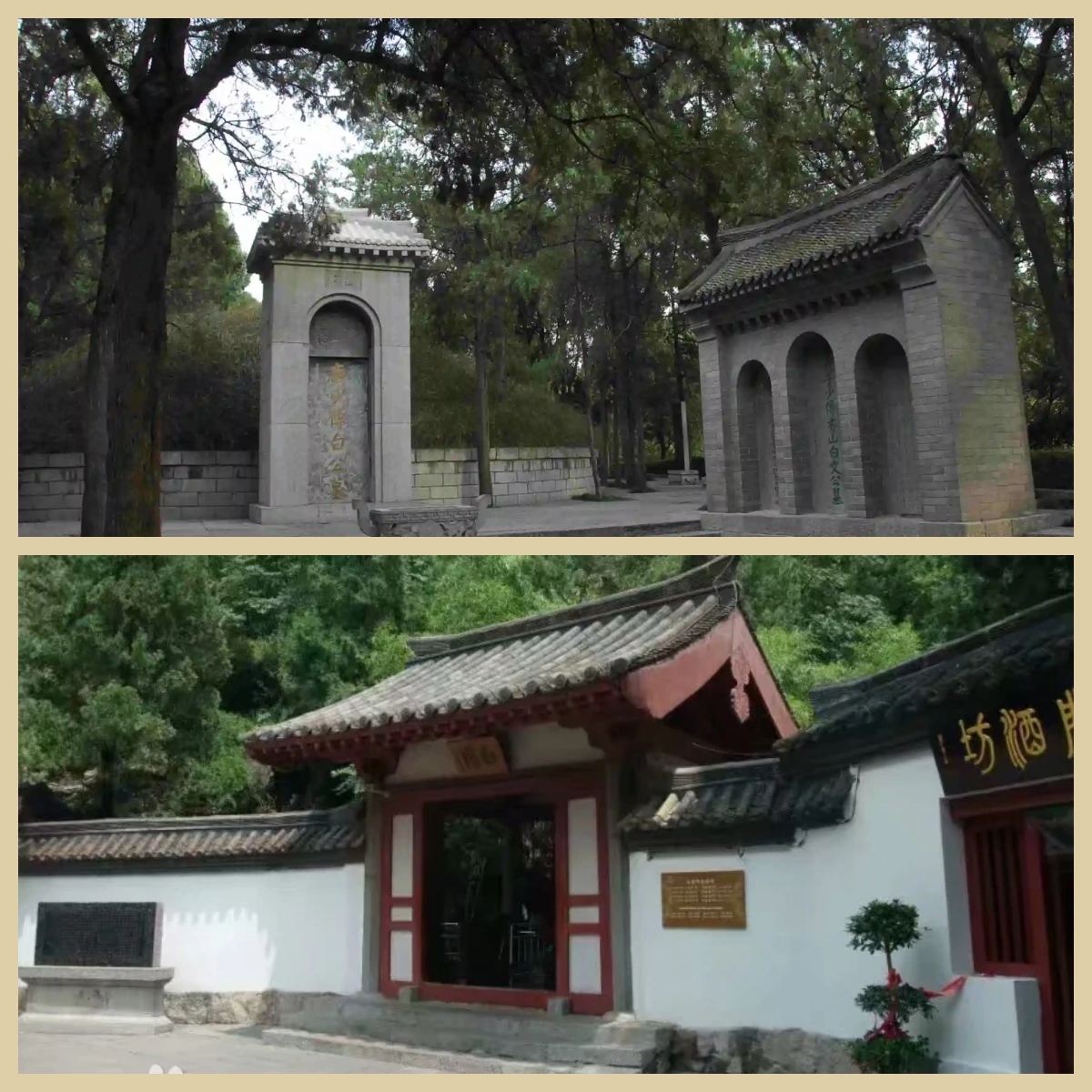
In addition, for certain relics that are severely damaged or completely missing and cannot be physically restored, the Longmen Grottoes Research Institute has utilized historical documents and image data to carry out digital restoration. By following specific reconstruction principles, they have been able to virtually restore the original appearance of these artifacts.
(For example: the Guanyin statue in the Wanfo Cave of the Longmen Grottoes.)
(SDG 17: Encourage cross-sector and interdisciplinary partnerships to advance cultural heritage protection and digital innovation)

Sustainable Development Goals

SDG 4: Quality Education/ SDG 6: Clean Water and Sanitation
SDG 11.4: Strengthen efforts to protect and safeguard the world’s cultural and natural heritage
SDG 13.1: Enhance resilience to climate-related hazards and natural disasters
SDG 13.3: Improve education, awareness, and human and institutional capacity on climate change mitigation and adaptation
SDG 17: Strengthen global partnerships to support the achievement of sustainable development goals
Reference:
1. All the images from Baidu:https://baike.baidu.com/item/%E9%BE%99%E9%97%A8%E7%9F%B3%E7%AA%9F/274
3.https://youtu.be/GsO2rC2aK1k?si=ww6J2YNkStvZtq30
4. UNESCO World Heritage Centre. (2000). Longmen Grottoes. [Online] Available at: https://whc.unesco.org/en/list/1003/
5. Getty Conservation Institute. (2021). Digital Preservation of the Dunhuang Caves.
6. United Nations. (2015). Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development.
7. Chinese Academy of Cultural Heritage (2018). Longmen Grottoes Conservation and Restoration Research. Beijing: Cultural Relics Publishing House.
8. National Cultural Heritage Administration (2023). List of Major Historical and Cultural Sites Protected at the National Level. Available at: https://www.ncha.gov.cn/
9.Dong Wang. “Internationalizing Heritage: UNESCO and China’s Longmen Grottoes.” China Information, vol. 24, no. 2, July 2010, pp. 123–147, https://doi.org/10.1177/0920203×10369097. Accessed 8 Dec. 2019.
10. Zhu, Jian, et al. A Study of Limestone from the Longmen Grottoes of Henan Province, China by Neutron Activation Analysis. Vol. 39, no. 7, 1 July 2012, pp. 2568–2573, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jas.2012.03.010. Accessed 16 May 2023.