Preserving the past. Protecting the future
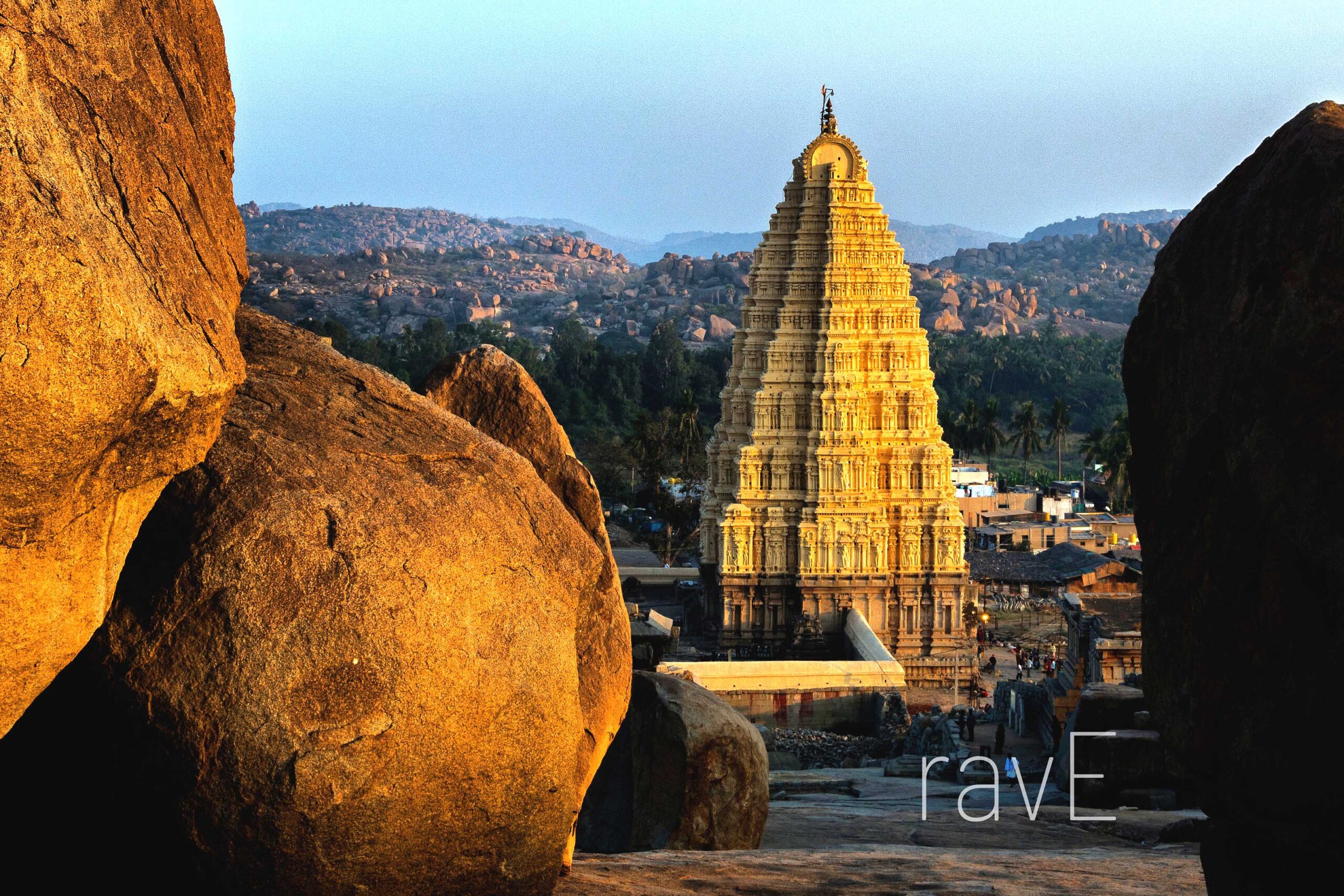
Hampi, situated in Karnataka, India, is a rich repository of India’s historical and cultural heritage, recognised as a UNESCO World Heritage Site for its extraordinary significance. Once a vibrant thriving capital of the Vijayanagar Empire between the 14th and 16th centuries CE, it stands as testament to the grandeur and sophistication of one the India’s most powerful medieval kingdoms. Traversing an expansive 4,100 hectares, this archaeological wonder showcases a diverse collection of is structures that represents the pinnacle of architectural work and artistic excellence of the era.
The site is well known for its monumental architecture, contains intricately designed temples dedicated to various gods/deities, sprawling royal complexes that once house of royal family and nobles, and civic buildings which supported the daily life of its citizens. These edifices are adorned by exquisite stone carvings and sculptures that emphasise the supremacy of Dravidian art. Beyond its artistic accomplishments, Hampi also exhibits advanced engineering through its advanced water management systems. These include meticulously constructed canals, tanks, and step wells that ensured efficient water supply and storage in a semi-arid landscape.
Hampi’s Urbanism reflects an in-depth understanding of medieval Indian city design principles with well-planned arcades and avenues. Its integration with city’s natural surroundings, rocky landscape adds another layer of exclusivity. Together, these elements make Hampi not just an archaeological site but also a living painting of history, art, and innovation that continues to inspire awe among visitors from around the world.
Walk Through Time: Explore Hampi in 3D
Step into the stone corridors and temple courtyards of Hampi with our interactive virtual tour. From the towering Virupaksha Temple to the iconic Stone Chariot of the Vittala Temple complex, this section lets you digitally experience the grandeur of Vijayanagar architecture as it stands—and as it once was.
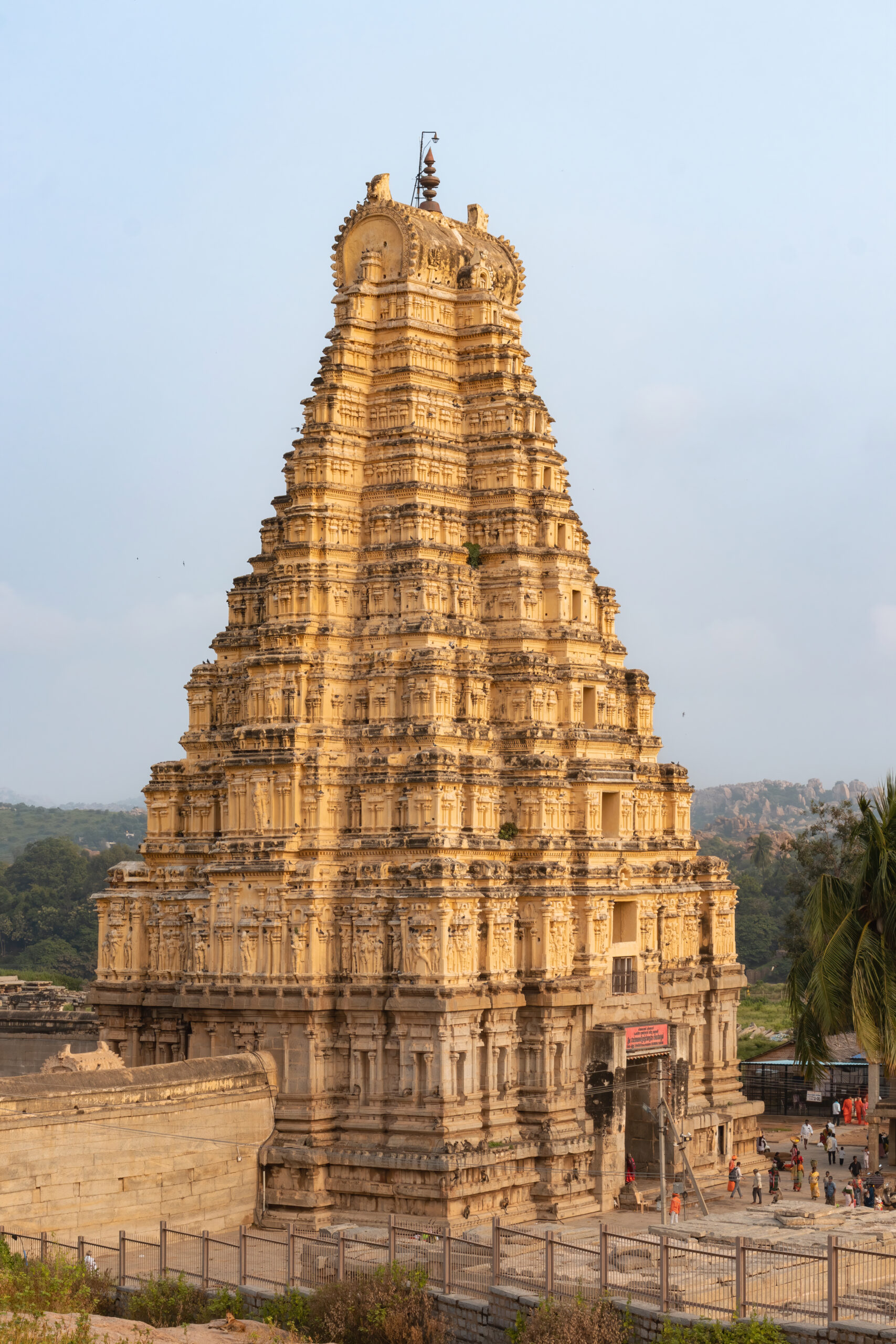

Virupaksha Temple: A living place of worship and a gateway into South India’s sacred architectural heritage.
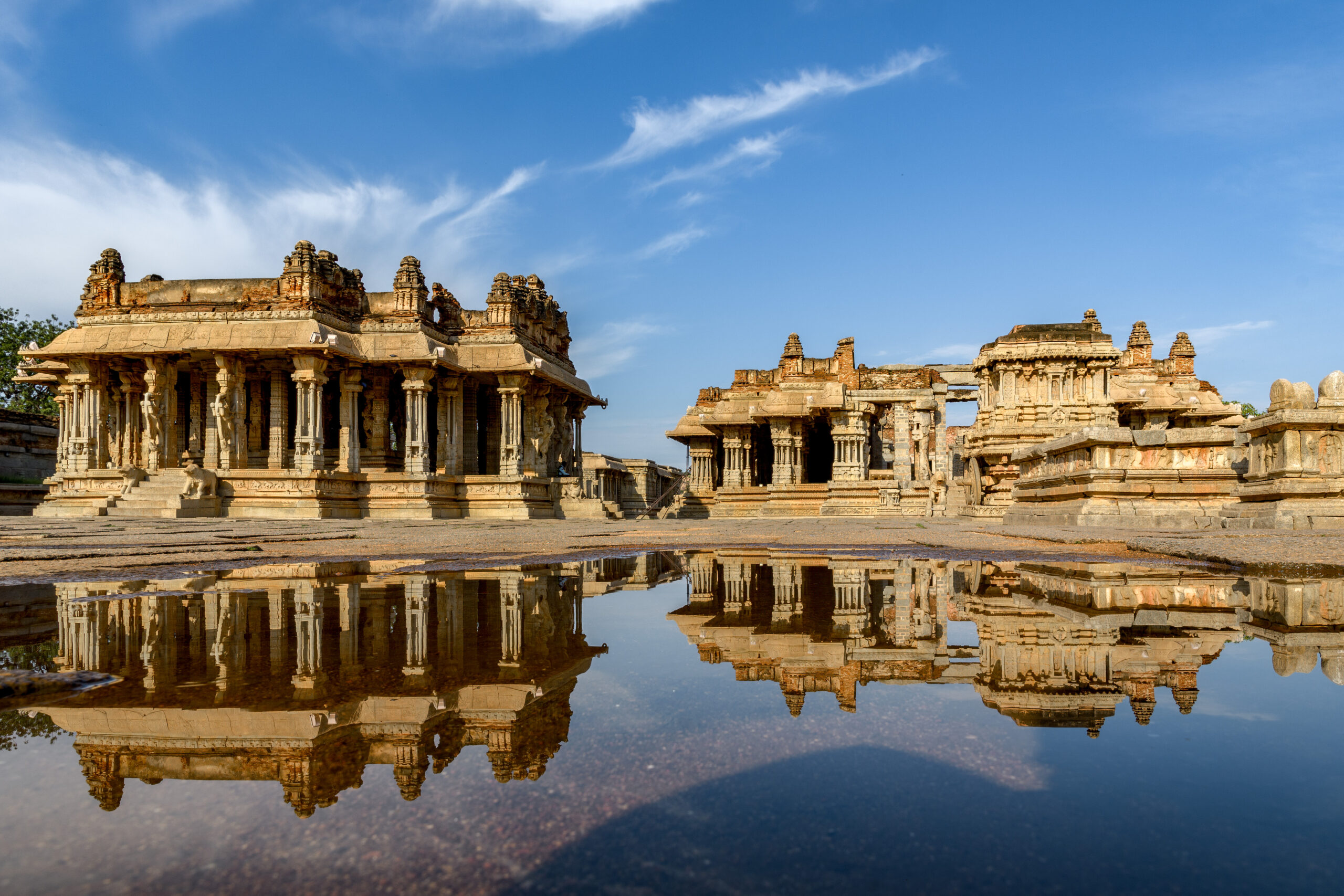

Vittala Temple: Famous for its musical pillars and chariot shrine – now threatened by erosion and flooding.
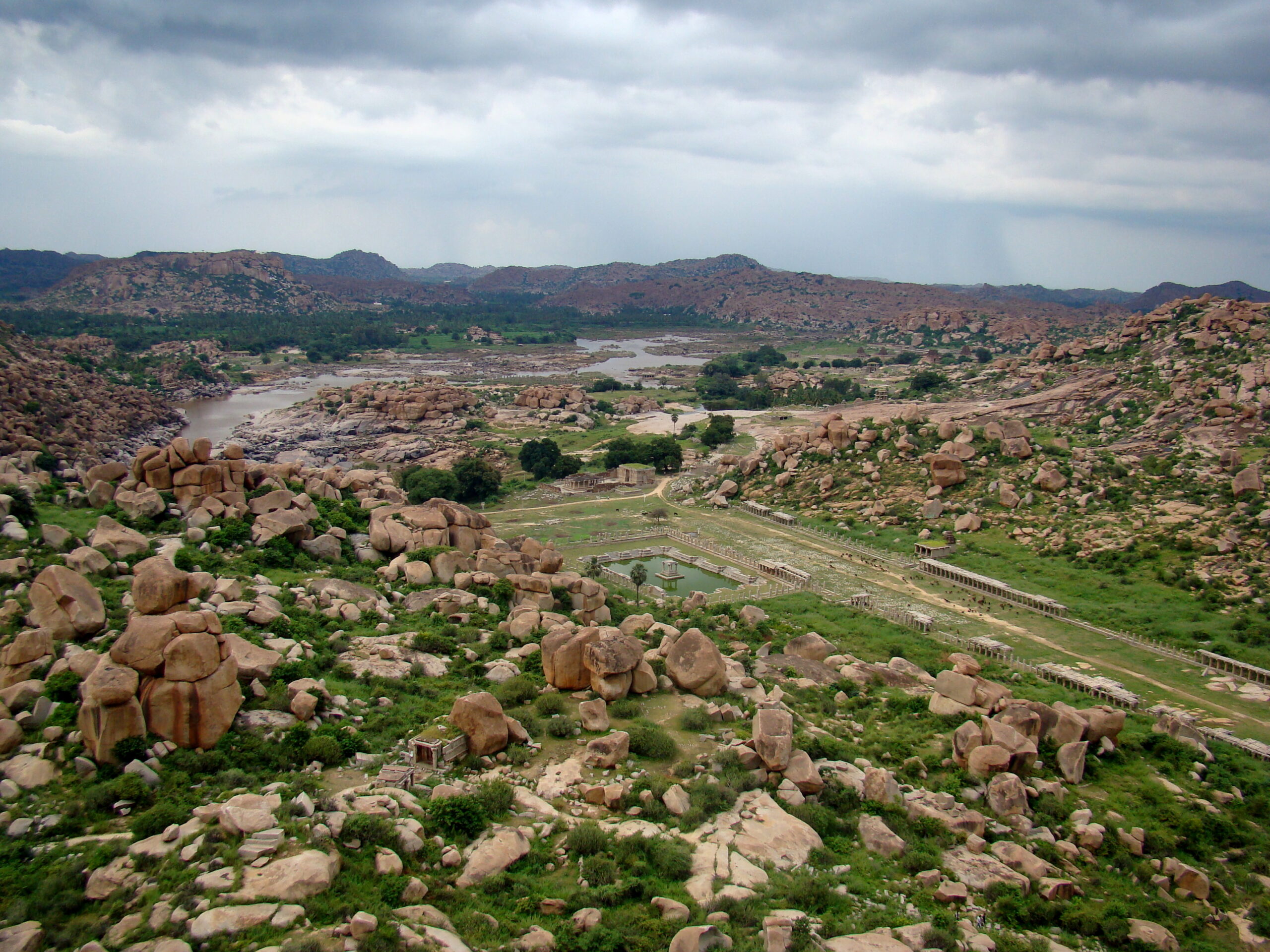

View from Matanga Hill: Vijayanagar market ruins, with Tungabhadra River in the background
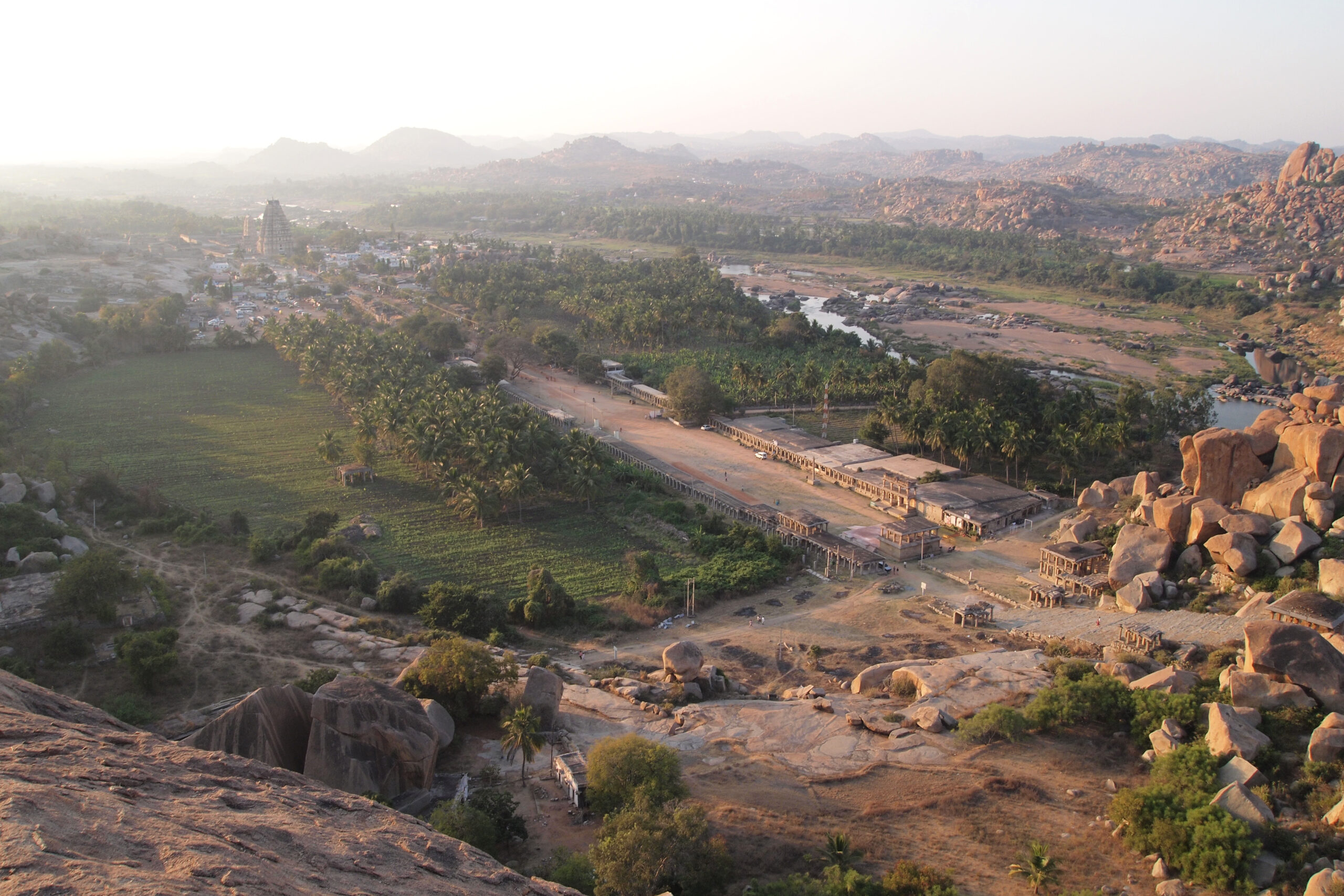

View from Matanga Hill: The highest point in Hampi, offering panoramic views of the ancient city.
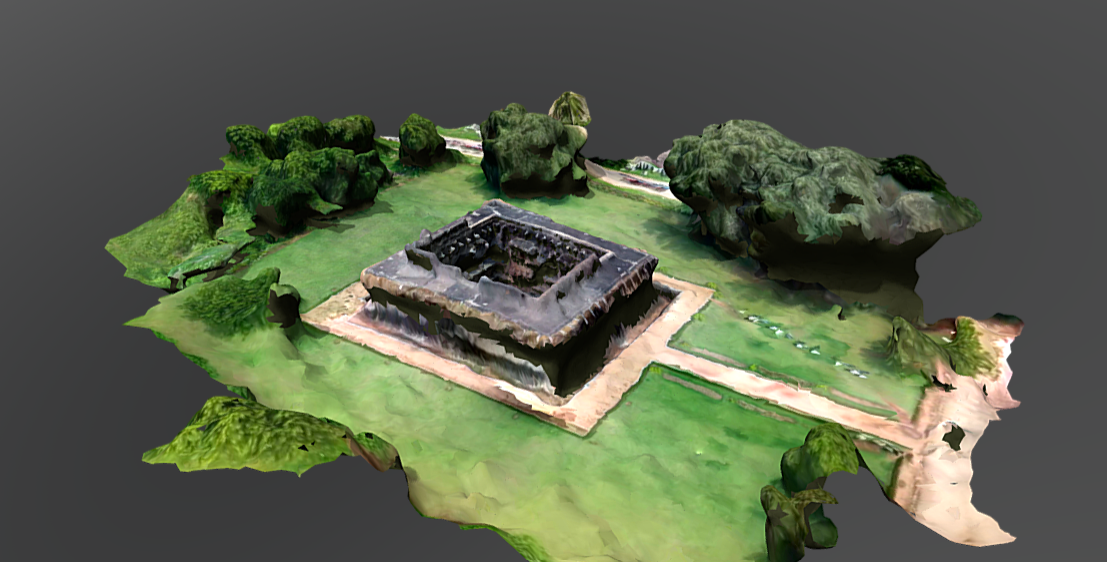

Hampi Snanagraha: 3D Scan from drone (Please follow the link in the caption for Sketchfab 3D view )
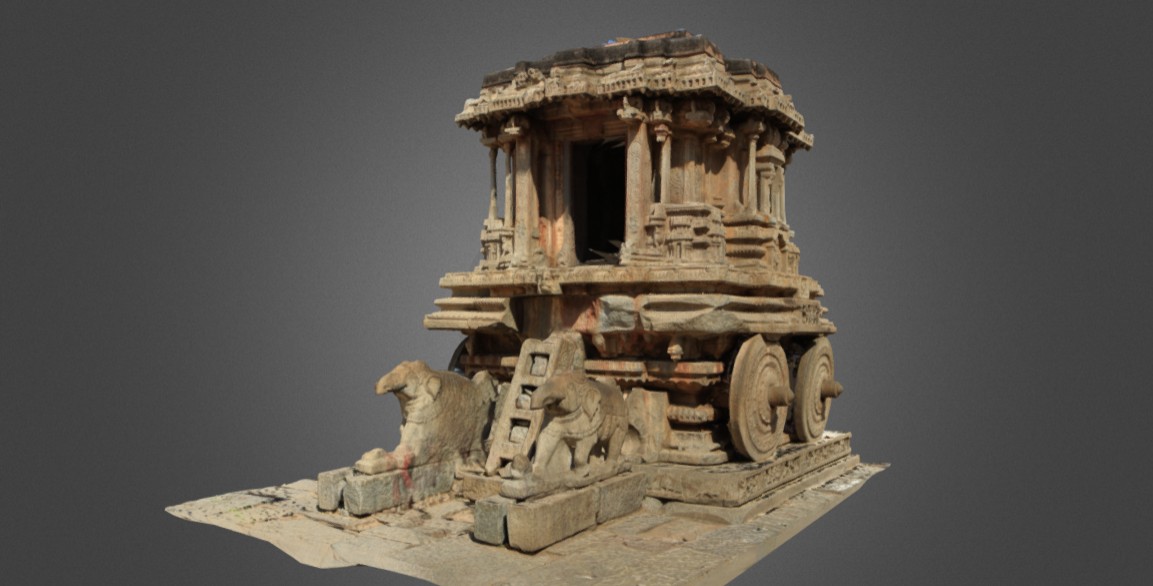

Stone Chariot in Hampi, India (Please follow the link in the caption for Sketchfab 3D view )
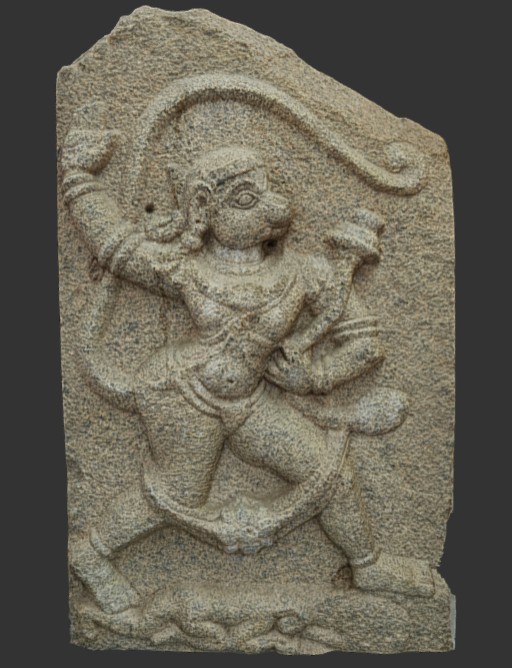
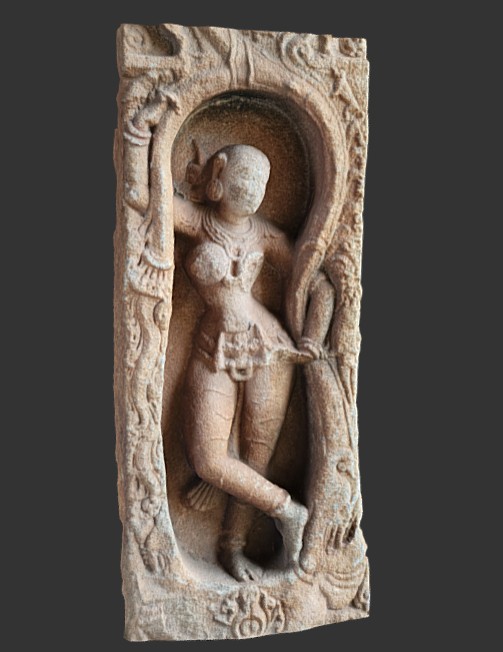


Statue and Mural Engraving from Hampi India (Please follow the link in the caption for Sketchfab 3D view )
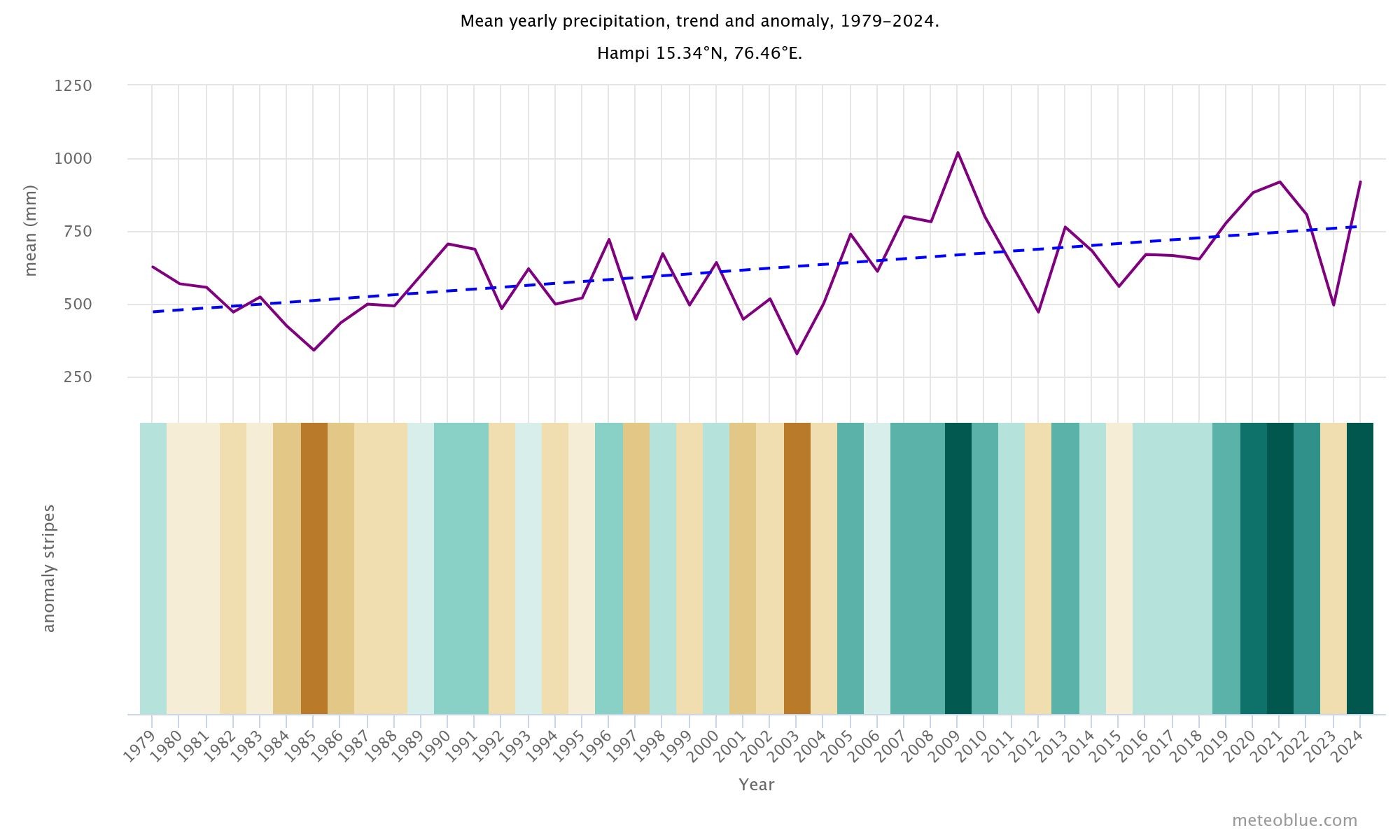
Climate Change Threats
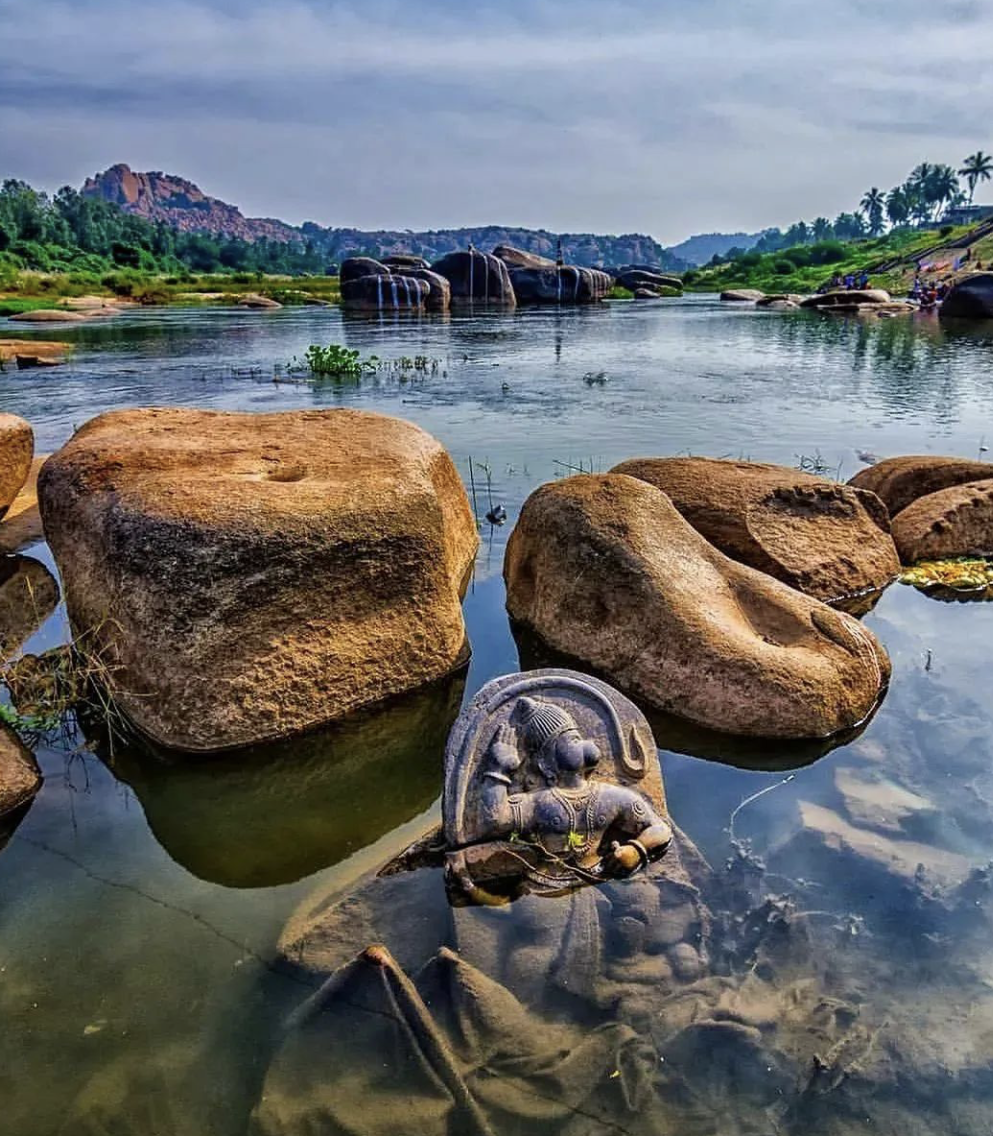
Flooding (Tungabhadra River)
Rising and erratic rainfall patterns have led to frequent and unpredictable flooding of the Tungabhadra River. When water levels surge, they endanger riverbank temples, displace communities, and accelerate the erosion of stone structures. These floods are no longer rare occurrences—they are becoming a seasonal reality.
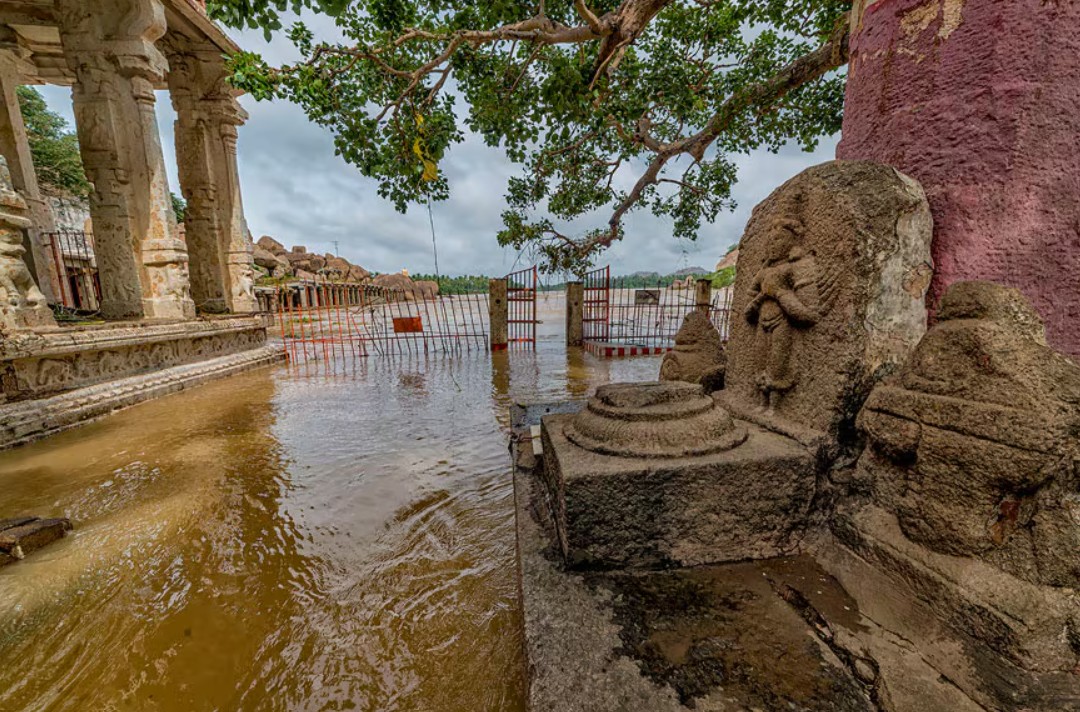
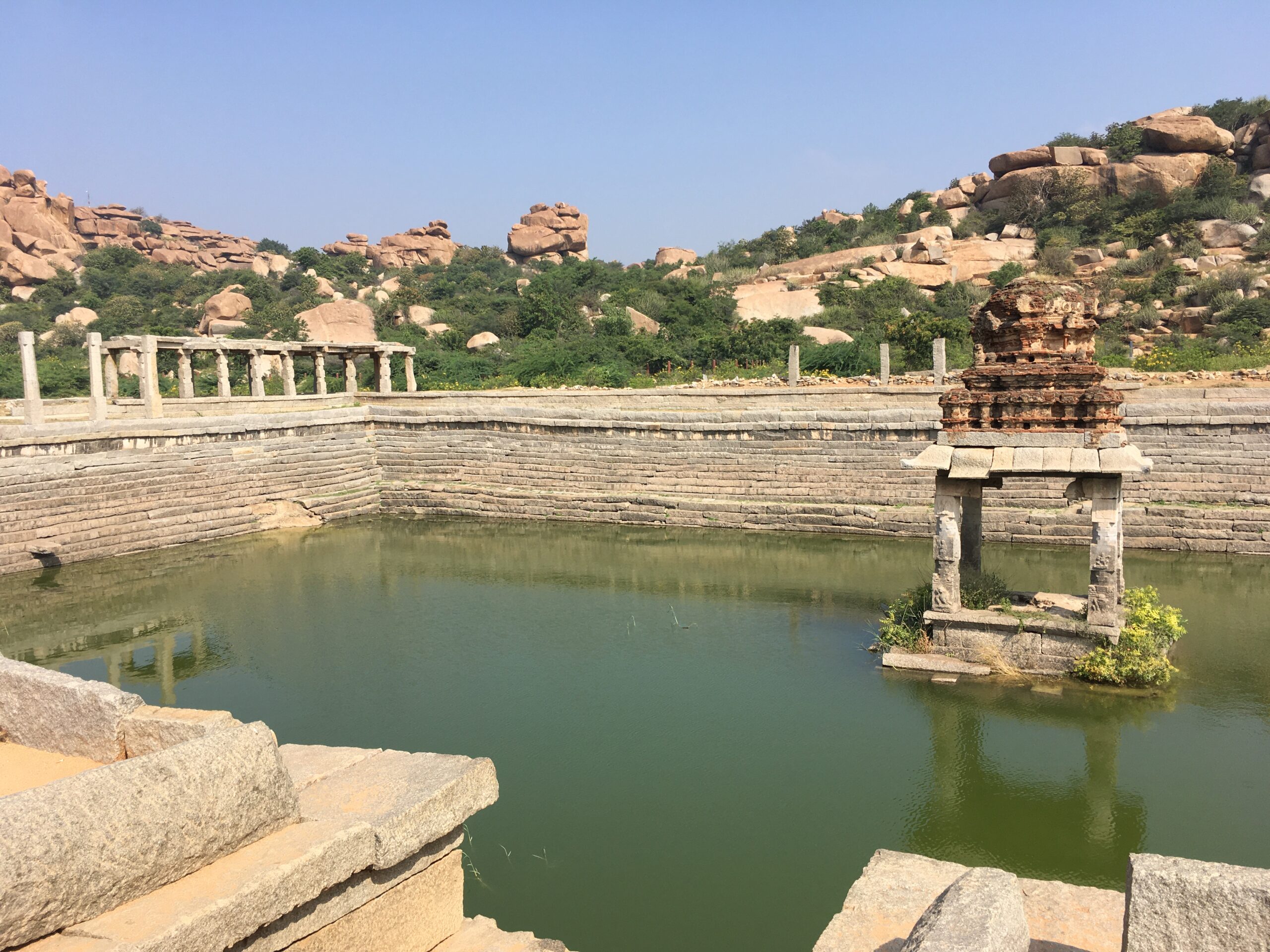


Droughts and Loss of Water Systems
Hampi’s historic water tanks and canals were ingeniously engineered to sustain life in a semi-arid landscape. Today, prolonged droughts and disrupted monsoon cycles are drying these systems out. As a result, traditional water infrastructure is falling into disuse, and the land loses its resilience to both drought and flood.
Salt Crystallisation from Rainfall
As rainfall becomes more intense and irregular, moisture seeps into the porous stones of ancient structures. When this water evaporates, it leaves behind salt crystals that expand and contract with temperature changes, causing slow but devastating structural damage to carvings, walls, and inscriptions.
Tourism Pressure
As climate-friendly travel seasons shrink, tourism is becoming more concentrated, placing added pressure on both infrastructure and the monuments themselves. Unregulated footfall, inadequate waste management, and commercial expansion threaten to erode the cultural and environmental balance of Hampi’s sacred landscape.
Biological Growth
Increased humidity and warmer temperatures foster the growth of algae, moss, lichens, and even small plants on heritage monuments. These organisms cling to stone surfaces, feeding on minerals and slowly breaking down the fabric of Hampi’s architecture, leading to discoloration and material loss.
Climate Change & SDGs Section
Quality Education (SDG 4)
Target 4.7- Education for Sustainable Development and Global Citizenship
Sustainable Cities and Communities (SDG 11)
Target 11.4 – Protect the world’s cultural and natural heritage
Climate Action (SDG 13)
Targets 13.1 – Strengthen resilience and adaptive capacity to climate related disasters
Targets 13.3 – Build knowledge and capacity to meet climate change
Partnerships for the Goals (SDG 17)
Target 17.17 – Encourage Effective Partnerships
Timeline & History Section
Let’s explore Hampi’s History through the media
Your Response Matters: Call for Action
Link for Google form : https://forms.gle/Rn1h2LyYdT4LUHTS9
Loading…