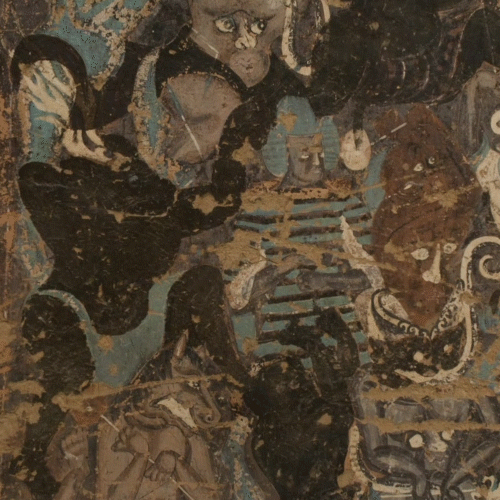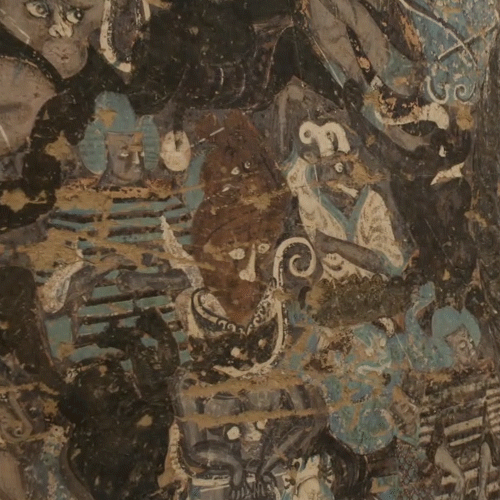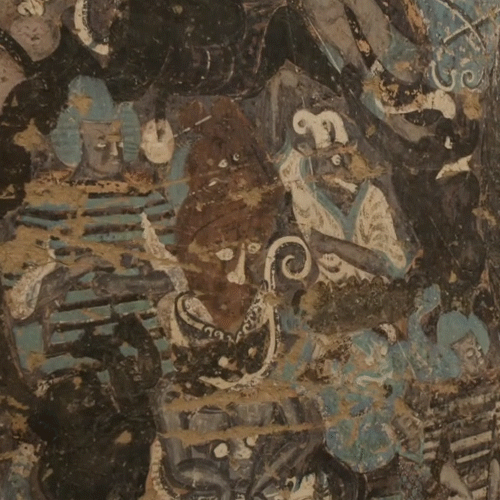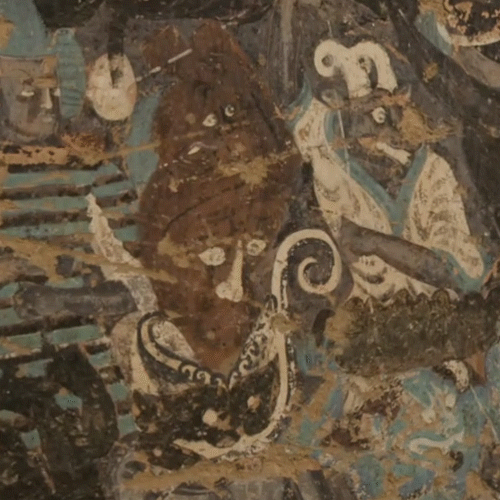Dunhuang Murals Virtual Exhibit




STAGE 1 – Multimedia Exhibition

_________________
Click here to see interactive prototype
The first part of this exhibition is the multimedia introduction module. After the user clicks to enter the exhibition system, they will first enter this module. This part introduces the relevant information of Dunhuang murals and the composition of the online exhibition to users in the form of text, images, and videos to guide users to further explore the exhibition.
Introduction
The Dunhuang murals are located in Gansu, China, with a history of more than two thousand years. These murals exist in 552 grottoes in Dunhuang, totaling more than 50,000 square meters.
Dunhuang murals art is a solid art combining architecture, sculpture, and mural. Although Dunhuang murals only play a role of decoration, and a supplementary role to the sculptures in the Grottoes, but they feature the greatest number, the largest scale, the finest art skills and the richest content, providing very valuable information and material for research on ancient Chinese politics, economy, culture, military, geography, communication, social life, national relationship, religious history, art history, and exchanges with foreign countries and history of cultural exchanges. It is indeed a classic art heritage of great value.


History of Dunduang Murals
The murals in the caves date from a period of over a thousand years, from the 5th to the 14th century, and many earlier ones were repainted at later points within the period. The murals are extensive, covering an area of 490,000 square feet (46,000 square metres). The most fully painted caves have paintings all over the walls and ceilings, with geometrical or plant decoration filling the spaces not taken by figurative images, which are above all of the Buddha. Sculpture is also brightly painted. The murals are valued for the scale and richness of content as well as their artistry. Buddhist subjects are most common, however some have traditional mythical subjects and portraits of patrons. These murals document the changing styles of Buddhist art in China for nearly a thousand years.
The painting style of the murals changed gradually in the following centuries, as traditional Chinese painting techniques such as line drawing replaced the imported ones. Maybe, it’s also because more Chinese artists had been employed to do the job, but no one seems to know for sure.
Content also changed over time. Instead of religious images and stories sometimes with a romantic touch, the murals began to adopt the realistic style that depicted the mundane life of people working in the fields, hunting, dining, singing and dancing or attending ceremonies for major holidays.

STAGE 2 – 3D Mural Models Exploration
Click here to see interactive prototype
The second part of this exhibition is the 3D mural model display. This module presents the collected rock mural information to the user in the form of a three-dimensional model. The user can zoom in and zoom out the model by operating the mouse or hand to view the details of the mural. At the same time, each three-dimensional model has a text information introduction corresponding to the mural.

STAGE 3 – VR Mural Cave Exploration

–
Click here to see interactive prototype
The third part is VR cave murals displaying. The virtual reality module simulates the environment of the actual cave where the Dunhuang murals are located, helping users to get a real cave browsing experience. After entering the VR exploration interface, users can choose to enter different caves to browse different murals. And users can click on a certain area of the mural to view the detailed information of the area according to their interests. The VR module is equipped with functions such as audio navigation and video playback to help users obtain an immersive browsing experience.
STAGE 4 – Interactive Entertainment
–
Click here to see interactive prototype
The fourth part is the entertainment interactive module. This module displays information about the exhibits related to Dunhuang murals in the form of interactive games and interactive videos. This module is equipped with interactive mural animation display and mural restoration interactive games, which could increase the entertainment and interest of visiting the exhibition and allow users to learn about cultural relics protection during the game.